
What is the Dark Web?
The Dark Web is often considered to be the most dangerous part of the internet. A subset of the deep web it cannot be indexed by traditional search engines. It is accessible with the right tools and can be extremely valuable if used correctly.
Before accessing the Dark Web it is useful to understand some of the key characteristics that are driving Dark Web growth. Let us first summarize where the Dark Web fits into the World Wide Web.
The Surface Web
The Surface Web consists of web sites that are accessible using a search engine and a standard browser (e.g., news sites, company public websites, online shopping sites).
The Deep Web
The Deep Web is a part of the surface internet not directly accessible through search engines but hidden behind a login wall or paywall (e.g., company network accessed via VPN)
The Dark Web
Access to the Dark Web requires specific technology, such as a proprietary browser or encryption program. For most people “the internet” or “web” consists of social media sites such as Facebook or Instagram and news sites that appeal to any point of view. The internet is a place where you can shop, find recipes and send grandad an email with a funny picture of a cat. What many people are unaware of is that the web they use, accessed through Bing and Google, is just a small part of the web as a whole.
This “surface” or “indexed” web can be considered the public face of the World Wide Web. Beneath this lies a much larger layer that consists of sites not indexed by search engines such as private databases, password protected sites and email services. This layer is often called the “deep web”. Below this, we come to the Dark Net.
The dark level of the internet consists of sites deliberately hidden from view using encryption. Why are these sites hidden? People often answer that it is because criminal activity is involved, otherwise why hide? A closer examination of the history of the dark web and its evolution reveals a more nuanced truth.
The Dark Net is not one network but a term that encompasses many services such as Tor, Freenet and I2P. These services provide decentralized, encrypted and anonymous internet communications making them popular tools for sharing secret or sensitive data for both legitimate and nefarious purposes.
The Tor Network
This article will concentrate on the Tor Network. Tor (The Onion Router) is easily the most widely known Dark Net (Freenet and I2P are other popular choices) and is frequently cited as an example of the disreputable side of the internet. Tor can be accessed through freely available software including a web browser that is very similar to Mozilla Firefox and provides even a novice user a high level of anonymity.
The browser allows users to access hidden sites with addresses consisting of random keys ending in .onion, as an example http://zqktlwiuavvvqqt4ybvgvi7tyo4hjl5xgfuvpdf6otjiycgwqbym2qad.onion is the link to “The Hidden Wiki” a page devoted to listing .onion sites. A standard browser such as MS Exchange or Chrome will not be able to access this page, a Tor enabled browser will render it as any other web page. An added bonus of a Tor enabled browser is that when you are browsing the Surface Web your activity is anonymized by encrypting your data and routing your communication through several “nodes” that hide your location and IP address.
The United States Naval Research Laboratory developed Tor in 2002 in order to provide a secure communication channel between U.S. intelligence agencies and their operatives in foreign countries. In 2015 it was then offered as a free service to encourage unrestricted access to the internet in situations where online censorship was intense or the threat of persecution for people seeking access to information considered illegal was prohibitive. The Tor Project still receives a majority of its funding from U.S government agencies such as the Department of State and the National Science Foundation. This support is justified by these agencies because Tor:
“provides potential life-saving online security and privacy in places – such as Iran and Syria – where political dissidents are often dealt with harshly”
There are persistent rumors and indeed some evidence that the Tor network still has ties to US intelligence agencies. However, papers leaked from the NSA indicate that compromising the Tor network is considered an extremely difficult operation and the Russian Internal Affairs Ministry has issued a government tender worth millions of rubles for anyone who can provide a reliable system to break Tors anonymity.
How Tor Works (Very simplified version)
The multi-layer encryption used by Tor has several advantages;
- The server receiving a request coming from the Tor network will only see the address of the last node it passed through (exit node). There is no simple way to find the origin of the request.
- Each node in the chain only knows the previous and following hop for a request and is unable to read the content or final destination.
- Only the exit node is able to view the content of the request however, the exit node does not know the original source only the preceding hop.
- Given the uptake in publicly available SSL encryption even the end node data can be hard to intercept.
Modes of Tor Use
A distinction needs to be drawn between the ways Tor can be used. Firstly, there is anonymous browsing or internet use where the user is simply accessing the normal internet but obfuscating their location and encrypting their communication. In this mode, users do not necessarily have nefarious motives. This form of anonymity protects users from Identity theft, reduces marketing surveillance and allows them to research topics that may be sensitive or embarrassing. Concealment of a user’s IP address is crucial for child protection or in a domestic violence situation. Over time our web browsing habits can be used to build a surprisingly details picture of our lives. Anonymous browsing can mitigate this risk. It has been calculated that up to 96 percent of Tor use is of this general browsing nature.
The second method of Tor use is providing or accessing a hidden service. These sites give the dark web its reputation of a den of identity thieves, drug dealers and paedophiles. However, perceptions are misleading. Many hidden services promote human rights, free speech and information prohibited in countries with repressive governments. The number of hidden services devoted to illegal activity is roughly the same as the number of hidden services dedicated to other subjects such as forums where drug users can get advice on safe use and domestic violence victims can come together for support. Given these numbers, the services dedicated to the most disturbing subjects such as murder and paedophilia would be a very small percentage.
The online markets of the Dark Net are practically the stuff of legend. The most famous, Silk Road was shut down in 2013 and other Dark Net markets such as Atlantis have disappeared under pressure by law enforcement. This shows that the anonymity of the dark Net is not the complete shield from law enforcement it is often made out to be.
Tor Good or Bad?
It is difficult to evaluate the good Tor provides and compare with the potential harm it produces. The ability to deliver safe, uncensored Internet access in countries like Iran, Russia and China needs to be balanced to to the possible harm created by the anonymous supply of drugs or firearms from an online black market. As well as the potential for harm minimisation by reduced violence and increased community, support. As mentioned previously Tor is just one of the many anonymising services available, were it to be compromised or shut down the activity on Tor, criminal or otherwise would quickly move to another possibly more secure anonymous platform. Given human nature one would have to come to the conclusion that if the dark Net did not exits, it would be invented tomorrow.
How to Access Tor
1. Download the installation file for your operating system and language at the Tor Browser Download Page.
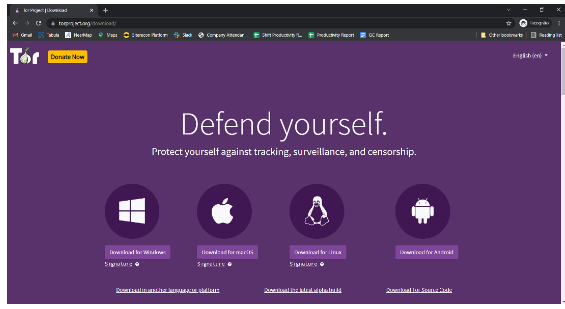
2. Run the install program.

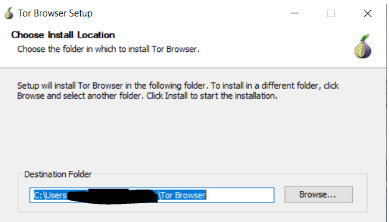
3. Choose the install location of the software. You will need about 220MB.
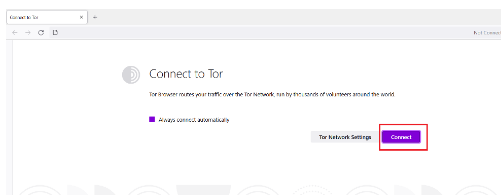
4. Open the Tor browser and click on Connect
3. When the browser is finished connecting to the Tor network a good place to start browsing is The Hidden Wiki. http://zqktlwiuavvvqqt4ybvgvi7tyo4hjl5xgfuvpdf6otjiycgwqbym2qad.onion The Hidden Wiki contains links to a broad cross section of hidden sites and advice that will give you a great starting point as you explore the “dark side” of the web.
A word of warning. While this article has tried to be balanced in its description and analysis of the Dark Web do keep in mind that it IS used by criminals and some pretty messed up people. If you explore very much some of the content you come across WILL be disturbing. Viewer discretion is advised..
Pingback: 5 Best Tools for OSINT Research - That Freaky New Guy